GIUSEPPE TOMASI DI LAMPEDUSA, IL GATTOPARDO: HOW TO CHANGE EVERYTHING, SO THAT EVERYTHING (ALMOST) REMAINS AS IT WAS.
A painful confession, to begin with: I have seen the Luchino Visconti (*1906-†1976) film version (1963)1 on many occasions), first time end of the 1960s, but I confronted the novel (1958, (Il Gattopardo, The Leopard) as such only last year, as chance allowed a translation into German to fall on my hands. The original Italian version was bought shortly afterwards2
A possible explanation for this décalage may have been the desire to read it in Italian, as I suspected that only the Italian text would suffice to let the images and sounds reverberate again, in the primaeval matrix, to confront, once more, that most precious of questions: Can a magisterial film subsume all the essence of such a novel? Provisional answer: A substantial part of it, yes, but some layers remain hidden in the texture of the novel. A not to be underestimated caveat: The film stops at the end of “Parte VI”, thus not incorporating “Parte VII” and “Parte VIII”, which take the action well beyond the 1860s, into the early 20th century. A tiny proportion of “Parte V” is incorporated as a dialogue of the Padre Pirrone with peasants in “Parte II”.
Both decisions are very clever, underlying the necessarily different ways of “handling” a novel and its “film version”. By limiting the action to the interval between 1860 and 1862, the “essence” of the novel is maintained, yet at the same time, the “saga” is kept compact and tense, as there are no “post-faces” stretching the narration over half-a-century which may dilute the core of the handling and the descriptions. A fuller integration of “Parte V”, which takes us with Padre Pirrone into his place of birth, would have been an unnecessary deviation from the “main stream”, the narration of the key events which underpinned the backbone of the text.
Thus this blog’s entry is an invitation, in particular to those who have seen the film, to read the novel, if possible in Italian. It would help to enjoy the cinematographic version even more, and to understand why there are descriptions and subdued allusions that cannot be transported onto the cinema-screen.
Visconti’s film (1963) is not only his capolavoro, it is one of the capolavori in the whole history of Italian cinema, and one of the greatest films ever made. Such accolades remain almost uncontested, as Visconti, as well as his camera and photography director, Giuseppe Rotunno (*1923-†2021) somehow managed to count on the technical advise of Rembrandt, Velázquez, Dürer, Caravaggio, Goya, Manet, Renoir et cetera… Try taking out almost any frame of the film, “frame” it as such, and hang it on the walls of any beaux arts museum: Nothing extraneous has been incorporated. The whole panorama is even enhanced.
A German edition
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Yet you cannot achieve such a pinnacle in cinema, unless the original source bathes itself in very high-carat. Indeed, the novel Il Gattopardo is one of the most fascinating, emblematic European novels of the 20th century. And perhaps also the most relevant in generating ex post, its own political theory regarding “continuity and change” in society: il gattopardismo.
Giuseppe Tomasi di Lampedusa (Palermo, 23 dicembre 1896 – Roma, 23 luglio 1957), “11º principe di Lampedusa, 12º duca di Palma, barone di Montechiaro, barone della Torretta, Grande di Spagna di prima Classe (titoli acquisiti il 25 giugno 1934 alla morte del padre)”3, could not see his beloved novel printed, having been refused by two major Italian publishing houses. It came out after his death, reaching a very large audience immediately, and it has been translated into almost every language. He was in no doubt as to the value of his opus, as transpired in his last letters before his death. Anyone reading the first pages in Italian would realise, at once, that we have in our hands a work of art into which the author had invested his soul, his blood, his remembrances, his dreams and his nightmares, to construct a fantastic, penetrating fresco of an epoch and of a family (his own, roughly speaking…), poetizing the landscape of Sicily to the point that we can smell the odours of the olives and the vineyards. We touch the salted drops of water of the Mediterranean, transported by the wind onto the arid hills and mountains of that land which had belonged to the Phoenicians, the Greeks and the Arabs. The Sicilians being the mixture of all that‒and much more. Let us just visit the “garden for the blind”, around the palazzo of il Principe de Salina:
“Era un giardino per ciechi: la vista costantemente era offesa ma l’odorato poteva trarre da esso un piacere forte ben che non delicato. Le rose Paul Neyron le cui piantine aveva egli stesso acquistato a Parigi erano degenerate: eccitate prima e rinfrollite dopo dai succhi vigorosi e indolenti della terra siciliana, arse da lugli apocalittici, si erano mutate in una sorta di cavoli color carne, osceni, ma che distillavano un denso aroma quasi turpe che nessun allevatore francese avrebbe osato sperare. Il Principe se ne pose una sotto il naso e gli sembro di odorare la coscia di una ballerina dell’Opera (Parigi), 4
“It was a garden for the blind: The eyes were constantly offended but the nose could draw from it a strong pleasure, albeit not a delicate one. The Paul Neyron roses, whose cuttings he had himself bought in Paris, had degenerated: Excited first and weakened later by the vigorous and indolent juices of the Sicilian earth, burned by the apocalyptic July, they had turned into a sort of flesh-coloured cabbage, obscene, but distilling a dense, almost indecent aroma that no French cultivator would have dared hope for. The Prince put one under his nose: He seemed to smell the thigh of a dancer from the Opera (Paris).”
None of the above was transposed onto the screen-it would have been almost impossible, had someone attempted it.
“Maggio 1860. “Nunc et in hora mortis nostrae. Amen”. La recita quotidiana del Rosario era finita.” Beginning of the novel and the film. 5 “The daily recital of the Rosary was finished.” from left to right: Padre Pirrone (Romollo Valli), Don Fabrizio Corbera, Prince of Salina (Burt Lancaster), Concetta Corbera, eldest daughter of il Principe (Lucilla Morlacchi), Princess Maria Stella of Salina, Don Fabrizio's wife (Rina Morelli). Il Palazzo Salina is in reality the “Villa Boscogrande” in Palermo.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This is not only a “historical novel”, it is a love-song to Sicily, with all its tremendous contradictions. Not to be forgotten: This is also a “Catholic novel”...
Most of the action takes place at the time of the Italian Risorgimento, centered on the commotion and upheavals caused by the landing of Giuseppe Garibaldi and his “proletarian” (but not only) army, known as The Thousand, I Mille di Garibaldi, on the Sicilian coast, May 1860. Soon they will overthrow the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies, run by the Bourbons, and integrate the island to a new, unified Italian Kingdom under Victor Emmanuel (Vittorio Emanuele II, *1820-†1878, as from 1861 “King of Italy”, “Padre della Patria”)
The mirror which reflects and reverberates all those changes is the Salina family, headed by il Principe Fabrizio, a tall, robust patriarch who imposes a strict Roman Catholic conduct and ritual upon its family, and devotes himself, together with Padre Pirrone, to science and astronomical observations, Don Calogero Sedàra which seemed to find some positive echo in Paris. He is actually of half German descent, half Sicilian.
“Ma nel sangue di lui fermentavano altre essenze germaniche ben più incomode per quell’aristocratico siciliano nell’anno 1860, di quanto potessero essere attraenti la pelle bianchissima ed di capelli biondi nell’ambiente di olivastri ed di corvini: un temperamento autoritario, una certa rigidità morale, una propensione alle idee astratte che nell’habitat molliccio della società palermitana si erano mutati in prepotenza capricciosa, perpetui scrupoli morali e disprezzo per i suoi parenti e amici che gli sembrava andassero alla deriva nel lento fiume pragmatistico siciliano.”6
"But
other Germanic essences fermented in his blood, much more
uncomfortable for that Sicilian aristocrat in the year 1860, however
attractive the very white skin and blond hair may appear in the
environment of olive trees and ravens: An authoritarian temperament,
a certain moral rigidity, a propensity for abstract ideas that in the
sloppy habitat of Palermo’s society had turned into capricious
arrogance, perpetual moral scruples and contempt for his relatives
and friends who seemed to him to swim adrift in the slow Sicilian
river of pragmatism.”
No, this is not “a Caravaggio”, albeit it seems, but a portrait of il Principe de Salina and Padre Pirrone, travelling to Palermo. “Che bel paese sarebbe questo, Eccellenza, se…”, “”What a nice country would be this, if…”, says Pirrone to il Principe, who interrupts him, “Se non vi fossero tanti Gesuiti!”, “If there weren't too many Jesuits!”7
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
His “alter ego” is composed of camouflaged sensuality and eroticism, which allows him to enjoy half-clandestine liaisons, be either in Paris or in the suburbs of Palermo.
“I ruderi libertini!”, “what a wrack of libertines!”, Tancredi (Alain Delon), to his uncle after a concealed naughty libertine night in Palermo.8
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Instead of taking refuge by the “British”, as his brother does on learning of the advance of Garibaldi and his soldiers, il Principe de Salina soon adopts a much more pragmatic, conciliatory attitude:
“Molte cose sarebbero avvenute, ma tutto sarebbe stato una commedia, una rumorosa, romantica commedia con qualche macchia di sangue sulla veste buffonesca. Questo era il paese degli accomodamenti, non c’era la furia francese; anche un Francia d'altronde, se si eccettua il Giugno del Quarantotto, quando mai era successo qualcosa di serio?”9
“A lot of things would happen, but it would all be a comedy, a noisy, romantic comedy with a few bloodstains on the buffoonish robe. This was the land of “arrangements”, there was no French fury; even in France, on the other hand, with the exception of June 1848, when had anything serious ever happened?”
“Se non ci siamo anche noi, quelli ti combinano la reppublica. Se vogliamo que tutto rimanga comme è, bisogna che tutto cambi. Mi sono spiagato?“10 Tancredi giving a formidable political lesson to his uncle, il Principe de Salina. “….Unless we take the lead again, those guys are going to concoct a republic upon us. If we want everything to remain as it was, everything needs to be changed. Have I made myself clear?”
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
That reflects also his way of handling employees and tenants, which combined distance, but also affection‒and tolerance. Be either by “ignoring” the cases of lemons which had been stolen by one of his devoted administrators, or “forgetting” to ask for the annual delivery of tributes in species from his tenants, specially when he visits Donnafugata, that refuge which allows him to escape from gossips and the skirmishes in Palermo, going there “to rusticate themselves”.
Padre Pirrone attempting to digest, without too much stomach-pain, the intimate confessions of il Principe de Salina, who has just been remonstrated because of his naughty escapade to Palermo. “Seven children I’ve had with her! (his wife) Seven! And do you know what, Padre? I have never even seen her navel…” Dialogue added by the screenwriters.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Entry of the family of il Principe de Salina into the Cathedral (Chiesa Madre) in Donnafugata, to assist at the traditional Te Deum offered to the family on its arrival at the town. Don Francisco "Ciccio" Tumeo (Serge Reggiani), organist and an old friend of il Principe, plays the melody of Violeta’s begging for love, Amami, Alfredo, in La Traviata of Giuseppe Verdi (*1813-†1901). The melody is also contained in the overture of the opera.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 |
No, this is not “a Rembrandt”. This is a scene in the cathedral, at the beginning of the Te Deum. On a wall outside one can read the inscription: VIVA GARIBALDO. It should have been “Garibaldi”, though in the novel it is written “Viva Garibbaldi”.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
To be noticed: The facial expression of Don Calogero Sedàra, mayor of Donnafugata (Paolo Stoppa), (left), who gazes at the Salina family, convinced that the moment has come, to seal an “alliance” between the slowly crumbling aristocracy and the ambitious new “bourgeoisie”, that is, an “alliance” between “prestige” and “money”. To be accomplished, as God disposes, only through “marriage”.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
A combination of Rembrand, Velázquez, and Dürer. The Salina family at its privileged position in the Cathedral, still bearing tonnes of dust accumulated during the journey.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
The long expedition (“Il viaggio era durato tre giorni ed era stato orrendo”11) in carriages of the family to Donafugatta, through the arid landscapes, where at times trees were unknown creatures, was perhaps one way of torturing themselves, or in the case of il Principe, that of paying for his sins. “Mademoiselle Dombreuil, “la governante francesa”, who had spent some years in Algeria could not contain herself: “Mon Dieu, mon Dieu, c’est pire qu’en Afrique!”12. There he would be received officially, with all the pomp the town could afford, by Don Calogero Sedàra, major of Donafugatta, a „self-made man“ rapidly accumulating wealth, fierce advocate of the “revolutionaries”, jet admirer of the Salinas, of awkward and inelegant manners, yet shrew and pragmatic. Her daughter Angelica will soon captivate Tancredi, the nephew of il Principe de Salina.
Angelica (Claudia Cardinale), only daughter of Don Calogero Sedàra, mayor of Donnafugatta, makes her entry into the sumptuous rooms of the Salina’s palazzo in Donnafugata. A hint of Pierre-Auguste Renoir but also Édouard Manet.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
“...ed entrò Angelica. La prima impressione fu di abbagliata sorpresa. I Salina rimasero col fiato in gola. Tancredi senti addirittura come gli pulsassero le vene delle tempie. Sotto l’impeto della sua bellezza gli uomini rimasero incapaci di notare. (…) Sotto la massa dei capelli color di notte avvolti in soavi ondulazioni, gli occhi verdi albeggiavano, immoti come quelli delle statue e, com’essi, un po’ crudeli. (…) recava nella persona la pacatezza, l'invincibilità della donna di sicura bellezza.”13
“… And Angelica entered. The first impression was one of dazzled surprise. The Salinas stood there with breath taken away. Tancredi even felt how the veins in his temples were throbbing. Under the impetus of his beauty, men were unable to notice. (...) Under the mass of night-coloured hair wrapped in gentle undulations, her green eyes gleamed motionless, like those of the statues and, like them, a little cruel. (…) She walked slowly (…) letting emanate from of her the calmness, the invincibility of a woman sure of her beauty. "
Reaction of il Principe de Salina…
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Reactions of Tancredi and of Concetta, one of the daughters of il Principe de Salina, who is supposed to be on her way to become, before long, Tancredi’s bride.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
The key dialogue between il Principe and Don Ciccio, while hunting early in the morning:
„La verità, Eccellenza, è don Calogero è molto ricco e molto influente anche; che è avaro (cuando la figlia era in collegio lui e la moglie mangiavano in due un uovo fritto) ma che quando occorre sa spendere.(…) ma un mese fa ha prestato cinquanta onze a Pasquale Tripi che lo aveva aiutato nel periodo dello sbarco; e senza interessi, il che è il pio grande miracolo che si sia visto da quanto Santa Rosalia fece cessare la peste a Palermo. Intelligente come un diavolo.“14
“The truth, Excellency, is that Don Calogero is very rich and very influential too; we know that he is a miser (when his daughter was at school he and his wife used to share a fried egg) but when something happens he knows how to spend (…) a month ago he loaned fifty “ounces” to Pasquale Tripi, who had helped him at the time of the disembarkation; and without interests, which is the biggest miracle to have been seen around here since Santa Rosalia extinguished the pest in Palermo. As intelligent as the devil…”
Don Ciccio, who voted “no” in the plebiscite (albeit no “no vote” was registered in Donafugatta would consider the “marriage” between Tancredi and Angelica as “treason, the end of the Falconeris (family of Tancredi) and even of the Salinas…“
The battle on the streets of Palermo. Please confront “The execution of Maximiliam” (1868/69) by Édouard Manet. And also “Los fusilamientos del 3 de mayo de 1808”, “Execution of the Citizens of Madrid”, completed by Francisco de Goya in 1814.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Battle on the streets of Palermo. Please confront “Los desastres de la guerra” (The Disasters of War), a series of 82 prints created between 1810 and 1820 by Francisco de Goya.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
The future husband of Angelica would return with a comrade, wearing the new uniform of the regular forces of the new Kingdom of Italy, making haste to distance themselves from the “proletarian revolutionaries”:
„Ma insomma, voialtri garibaldini non portate più la camicia rossa?“. I due si voltarono come se li avesse morsi una vipera. „Ma che garibaldini e garibaldini, zione! Lo siamo stati, ora basta“ (…) Con quelli lì non si poteva restare (…) Mamma mia che gentaglia! Uomini da colpi di mano, buoni a sparacchiare, e basta!“15
„But, after all, you the garibaldini no longer wear the red shirt?” The two turned around as if a snake had bitten them. “But, uncle, forget the garibaldini and garibaldini! We had been, and now it is all over. We could not have possibly remained there with those guys! Mamma mia, what a mob! Good for ambushes and looting, and that’s all!”
Sharply attacked by the Italian Communist Party (to which Visconti felt very close) when it was first screened, the film was accused of being “politically conservative”, expressing a “reactionary ideology” by more or less by the whole spectrum of the Italian left16. Visconti even concocted a different version, adding much more references to the “class struggle” and the “peasant resistance” (which were eliminated of the version presented at the Venice Festival), but even that concession did not seem to placate the vociferous critics, the insistence being upon “il anti-storicismo” of the film. That the vision-of-the-world transpiring out of the novel, and out of its cinematographic translation, was one of rejecting the possibility of “progress”, or “real changes” taking place in society. Or at least in Sicily.
Should that really be the final conclusion to be extracted? Does the statement “...If we want everything to remain as it was, everything needs to be changed…” really implies that “revolutions” are much more “superficial” than what they appear at first? No one could possibly imagine that Giuseppe Tomasi di Lampedusa attempted to deny the possibility of change, the inevitability of at least some “progress” taking place, albeit perhaps at much slower rhythm.
I happen to believe that the gattopardismo should not be interpreted as a cynical approach to history, insisting on the futility of “vociferous and radical speeches”, and even of thunderous street battles and brief, or even long, “civil wars”. It is rather the conviction that there is a constant need to find a new “equilibrium”, let us call the “Lampedusian equilibrium”, that there is an innate trend in society to “re-arrange” the bits and pieces, to find a new way of “coexistence”. In the concrete case of this Sicilian novel, it means probably that:
“...the upper classes agree to behave a “little less conservative”, and the “revolutionaries” agree to behave much more “less revolutionary”...
“...e il giorno del matrimonio consegnerò allo sposo venti sacchetti di tela con mille “onze” ognuno…”17 Don Calogero enhancing the pre-nuptial deal between Tancredi and Angelica, by “...on the day of the wedding I shall give to the bridegroom twenty linen sacks, each of them containing 1,000 ounces of gold…” Padre Pirrone “monitors” the whole transaction, while “reading” unobtrusively in a corner.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Angelica yearning for the long-awaited, just-about repressed first intimate communion with her fiancé, while playing and exploring the labyrinth of forgotten and uninhabited rooms and corridors in the Salina’s palazzo in Donnafugata, which constitutes in fact “il nucleo segreto centro d’irradazione delle irrequietudine carnali del palazzo...”18, the secret core, the centre of the radiations of the carnal anxieties of the palazzo…”
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
And those days, playing like excited children and caressing the frontier of sensuality, but not trespassing it, were to constitute the best moment of their lives:
“Quelli furono I giorni migliori della vita di Tancredi e quella di Angelica (…) Quando furono divenuti vecchi e inutilmente saggi I loro pensieri ritornavano a quei giorni con rimpianto insistente: erano I giorni del desiderio sempre presente, perché sempre vinto, dei letti, multi, che si erano offerti e che erano stati respinti, dello stimolo sensuale che appunto perché inibito si era, un attimo, sublimato in rinunzia, cioè, in vero amore.”19
"Those were the best days of Tancredi's life and that of Angelica (...) When they became old and uselessly wise, their thoughts returned to those days with insistent regret: they were the days of ever-present desire, because always conquered; of beds, many of them, which had offered themselves, and which had been rejected; of the sensual stimulus which, precisely because it was inhibited, was, for a moment, sublimated into renunciation, that is, into true love. "
21 pages, between pp. 211-232, in the novel are used to describe the „ball“ in the palazzo Ponteleone (in the film the location is the palazzo Valguarnera-Gangi, in Palermo). That represents about 10 percent of the pages of the novel which were “screen-written” in the film. Yet the screen version of that sequence occupies almost one third of the length of the film.
“The impossible love”, il Principe de Salina dancing a waltz with Angelica (at her request…), letting eyes and words communicate that well-hidden, unspoken desire. Tancredi watches that dancing exhibition, just about containing jealousy and fear.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Is that a disproportionate “zoom-in” of such a tiny proportion of the text? Not quite, although there is no doubt that Visconti and his teams decided to widen that evening at the palazzo Ponteleone, fist of all, in order to apply a sumptuous choreography, and let glittering attires, whose colours had been meticulously premeditated, glide before our eyes, as an incessant flow of images, as if the best tableaux of the best museums have been joint together, and let to float around, distilling gold and silver:
“the ball in the palazzo, which runs as a favourite in the competition to designate the most beautiful film-sequence of all time…”20
Visconti also extends the “ball scene” to let it operate as a magnetic field, a reverberating human landscape of all the Leitmotiven, the themes of the whole novel. It is the “presentation in society (high)” of Angelica, and even of her father, whose clothes have been selected by his future son-in-law. It is the reunion of il Principe de Salina with his relatives, and even with his former lovers. The new military officers turn in, who in the next early morning are going to execute the “rebel soldiers”, those who did not want to let the “revolution” fade away. The new Lampedusian “equilibrium” is consecrated and rejoiced.
The young ladies kicking around, sitting, or even jumping like pigeons caught in a whirlwind of desires and excitements, letting their fans act as wings, the colours of their dresses representing a harmony a white, orange and gold, almost a reflection of the walls in which they celebrate the evening.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
It is the mingling and contrast between “youth” and “old-age”, the awareness of the brief splendour of gallantry and vanity, and the inevitability of death.
A perfect composition of colours: white, then dark-blue, crowned by the red roses.---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
“...la carrozza se fermò; si sentiva un gracile scampanellio e da una svolto comparve un prete recante un calice col Santissimo; dietro un chierichetti gli reggeva sul capo un un ombrello bianco ricamato in oro; davanti un altro teneva nella sinistra un grosso cero acceso, e con la destra agitava, divertendosi molto, un campanellino di argento. Segno che una di quelle case sbarrate racchiudeva un’agonia, era il Santo Viatico. Don Fabrizzio scese, s’inginocchio sul marciapiede, le signore fecero il segno della croce, lo scampanellate dileguò nei vicoli che precipitavano verso S. Giacomo, la calèche con i suoi occupanti gravati di un ammonimento salutare s’incamminò di nuovo verso la meta ormai vicina.”21
“... the carriage stopped; a feeble ringing was heard and a priest carrying a chalice with the Blessed Sacrament appeared from a corner; behind him followed an altar boy, who held a white umbrella embroidered in gold over his head; in front of him another held a large lighted candle in his left hand, and with his right he waved a silver bell, very much amusing himself. A sign that one of those barred houses enclosed an agony, it was the Holy Viaticum (Last Sacrament). Don Fabrizzio got out, knelt on the pavement, the ladies made the sign of the cross, the bells disappeared in the alleys that rushed towards S. Giacomo, the calèche with its occupants, burdened with a salutary warning, set off again towards the destination, now quite close."
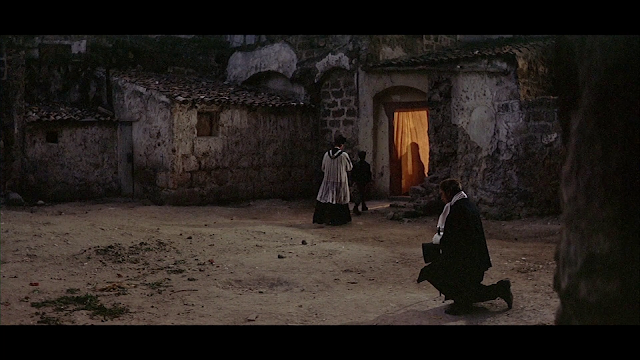
What does a man do, even if he were to be a “Leopard”, when he realizes that youth has gone for ever, that the sensual pleasures have lost their intoxicating initial splendour, and no longer constitute the compass of daily life?
He does as follows:
Final scene of the film: Il Principe de Salina, having... kneels down in a modest suburb of Palermo. In the novel this scene comes before the Salina family arrives at the ball, not after.
1We refer here to the 185 minutes version, the one presented in Venice. Initially it was 205 minutes, then 195 and finally 185. The US version was 161 minutes.
2Il Gattopardo, Giuseppe Tomasi di Lampedusa, Nueva edizione riveduta a cura di Gioacchino Lanza Tomasi. UNIVERSALE ECONOMICA FELTRINELLI, Milano, 2021.
3Wikipedia, Italian.
4P. 35.
52021, p. 31. Unless otherwise indicated, all translations from Italian into English are by the author of this blog.
6P. 33.
7P. 45.
8P. 49.
9P. 55.
10P. 50.
11P. 75,
12P. 70.
13P. 91.
14PP. 126-27.
15P. 155.
16Wikipedia (Italian)“Il film fu osteggiato anche dal Partito Comunista Italiano (al quale era legato Visconti) che non vedeva di buon occhio il romanzo di Lampedusa, ritenuto "espressione di un'ideologia reazionaria" e "politicamente conservatore".[15] Per questo motivo il regista montò una versione alternativa per la critica cinematografica della sinistra di area comunista, che includeva alcune scene del tutto estranee al romanzo originale ma molto conformi alla sua salda fede marxista, come conflitti di classe e fermenti di rivolta contadina[16], poi tagliate nella versione definitiva presentata al Festival di Cannes. Questo non bastò a risparmiare le critiche di alcuni intellettuali di sinistra che bollarono il film di anti-storicismo.[17]
17P. 138.
18P. 163.
19P. 165.
20The Leopard. (https://www.rottentomatoes.com/m/the_leopard_1963/) In: Rotten Tomatoes. Fandango, abgerufen am 22. Oktober 2017 (Englisch).
21P. 213.